- A-29, Industrial Area, Site IV,
Sahibabad, Ghaziabad, UP, India. - (+91-120) 2896063
info@bhartiyagroups.com

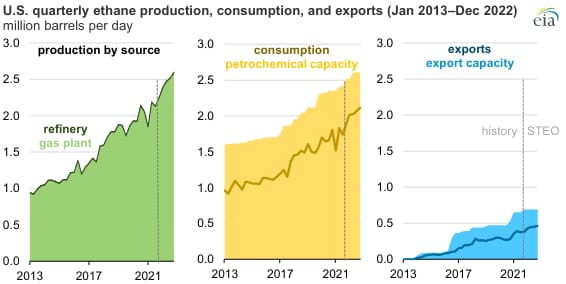
Anybody who follows the oil and gas business in the USA knows that ethane is presently abundant and affordable. The massive development of unconventional shale development in the United States has coincided with an exceptionally rapid increase in the Cryogenic oxygen plants and ethane has been by far the least priced and most abundant natural gas liquid found in the relatively "wet" hydrocarbons.
Due to the obvious high cost of aromatics, corporations in the United States were shuttering their massive cracker operations not long ago. It was before shale development made it possible to manufacture oil and natural gas liquids and manufacture of oxygen plants, most notably ethane, at a very minimal cost. Today, new drilling regions are being discovered in both "old" plays like the Permian and "new" ones like with the Marcellus, Eagle Ford, and Bakken plays, as well as new formations being identified beneath well-known formations.
The United States is extremely rich in hydrocarbons, and now it has the technological potential to manufacture them economically without relying on imported oil.
When you consider that our neighbors to the north are likewise rich in hydrocarbons, and our southern neighbors have opened up their hydrocarbon potential to privately owned business, our abundance position looks much stronger.
What will be used to absorb excess supply?
There is currently a big gap between obtainable ethane and the market for its own usage, with more ethane available than it can be consumed. Ethane crackers (which produce ethylene) are costing tens of billions to develop; seven are under construction in the Gulf Coast area, and more are being announced.
Ethane's primary value remains in it being used as a petrochemical feedstock around the world, which would no doubt absorb some more of the excess ethane, particularly as exporting and importing infrastructure continues to improve, petrochemical plants switch to ethane from competing feedstocks, and the price of ethane (including shipping costs) tends to be low.
Ethane ships of a new size—
VLECs (Very Large Ethane Carriers) have been built, those that are in the process of being built, and others have been already deployed to transport ethane from the United States to Europe and other places around the world to be used in the manufacture of plastics.
However, petrochemical feedstock it's not the only thing which can assist in absorbing the oversupply.
There are many other users and applications which can be developed or served better.
The ethane specialized market is a segment that is underserved.
"There was an additional market," says Don Bobyk, Vice President of Marketing at Gas Innovations, "that incorporates ethane requirements who have not yet evolved enough—and indeed have not yet been expected to progress based on supply—to require pipeline or shipload quantity."
This market is now underserved leading to a shortage of suitable oxygen cylinder filling plants, and our business has stepped in here to fill the void with our relentless pursuit of a trustworthy oil supplier."
"We refer towards this new industry as the ethane special market for simplicity's sake," explains Gas Innovations Executive Vice President Ashley Madray, "and we classify the market's applications into 3 categories: refrigerants, specialty gases, and BTU supply."
This market necessitates specialist knowledge, technology, and packaging, which we believe our company excels at.
Refrigerants
In some ways, the refrigerant business is still very much in infancy, and it is likely to grow significantly in the near future. LNG plants are resuming construction, and liquefaction technology has evolved to the point that ethane is a preferred refrigerant in some instances due to its inclusion in NGLs in the event of an incident. Large amounts are typically required for start-ups and black stars, as well as in the event of leaks whenever the oxygen liquid plant lacks the capacity to create its own ethane.
In summary, the following are amongst the global refrigerant applications:
• LNG facilities—the use of ethane as a refrigerant in the manufacturing of LNG (for example, Gas Innovations supplied Chevron's Gorgon project).
• A "naturally occurring" refrigerant which can be used in commercial, industrial, and commercial applications to replace CFCs, HFCs, and HCFCs.
Specialty gases
The specialty gases segment had already been starting to grow in previous years, but this has been stifled during the last year due to the disappearance of a key source of ethane supply, forcing customers and potential customers to look for alternative products or put their own projects on hold until an appropriate oxygen plant supplier becomes available.
(Gas Innovations is now assisting in filling the void.)
In light of the global market, applications in the specialty gases segment are expected to grow.
Include examples like these:
- Engine testing (converting turbines,
diesel engines to ethane)
- Experimental, R&D testing
- Petrochem pipeline support (during interruptions)
- Small specialty and fine chemical supply
- Large chemical supply where pipelines are not available – tanker, shipload, or railcar quantities are used
- Oil and gas well fracking
- Enhanced oil recovery (EOR)
Staffing requirements:
• General safety training – PPE, hazard identification, product training, equipment training, and security protocols
• Cryogenics and high-pressure gases expertise; documented training, testing, and observation
• In-depth knowledge of each box being filled (DOT requirements and container requirements)
Plant equipment requirements –
Cryogenics, liquefied compressed gas, High-pressure gas:
- Cryogenic tanks
- High-pressure liquid pumps, high pressure gas compressors
- High-pressure storage tubes
- Vacuum pumps, fill racks, associated
Equipment
- Full-size truck scales
- Full-service laboratory
- Tractors
SPECIAL FEATURE
- Low-pressure cylinders (ranging from 5
Pounds to 435 pounds)
- High-pressure cylinders (ranging from 1,800 psi to 6,000 psi maximum work pressure)
- Cryogenic tankers (10,000 gallon)
- High-pressure tube trailers (to 3,600 psi)
- Bulk trailers (hydrocarbons; to 11,000 gallon)
- Cryogenic ISO (6,000 gallon)
- ISO high-pressure tubes (for high-pressure gas or liquefied compressed gas) (15,000 pounds)
- Low-pressure ISO bulk (6,000 gallon, often 22 bar or less, single-hulled)
- Railcars – cryogenic, bulk, high-pressure tubes (owned by Gas Innovations but utilized by them)
- LPG, ethane, and LNG ships (not owned by Gas Innovations, but used by them)
Gas Innovations provides a solution to a problem. Customers who would like to start small, prove technology, and then scale up to the higher volumes that require larger packaging, pipelines, or factories have already been blocked until recently.
Because of a shortage of supply, both in terms of continuity and in terms of supply composition, this developmental-stage market had really been stalling (cryogenic, liquefied compressed).
Ethane Market, Ethane Supply, Oxygen Cylinders, Refrigerants, Liquefied Compressed Gas, Cryogenic Tanks, Low-Pressure Cylinders







